What Do Dabs Look Like: A Complete Guide to Cannabis Concentrates

Understanding the vast world of cannabis concentrates can be overwhelming. Did you know, for example, that dabs are highly potent forms of marijuana extracts? This guide will navigate through what dabs look like, their types, and how they're made to clear your confusion.
Get ready to become an expert on all things dabs.
Key Takeaways
- Dabs are concentrated forms of marijuana that come in different types like oil, shatter, wax, budder, and live resin. Each type has its own look and texture.
- Making dabs involves using solvents to extract THC from cannabis plants. Methods include butane hash oil (BHO), CO2 extraction, rosin press, ice water extraction, and solventless mechanical extraction.
- The process of dabbing allows for quick and potent effects due to the high concentration of THC. However, it's important to start with small doses because of the intensity.
- After making dabs, producers clean up any leftover solvents through processes like purging in a vacuum oven or winterization with ethanol. This ensures a safe and pure product.
- While dabbing offers powerful benefits like fast relief and strong flavors from diverse terpene profiles, there are risks such as potential health hazards from high THC levels and legal issues depending on where you live.
What Are Dabs and How They Are Related to Marijuana
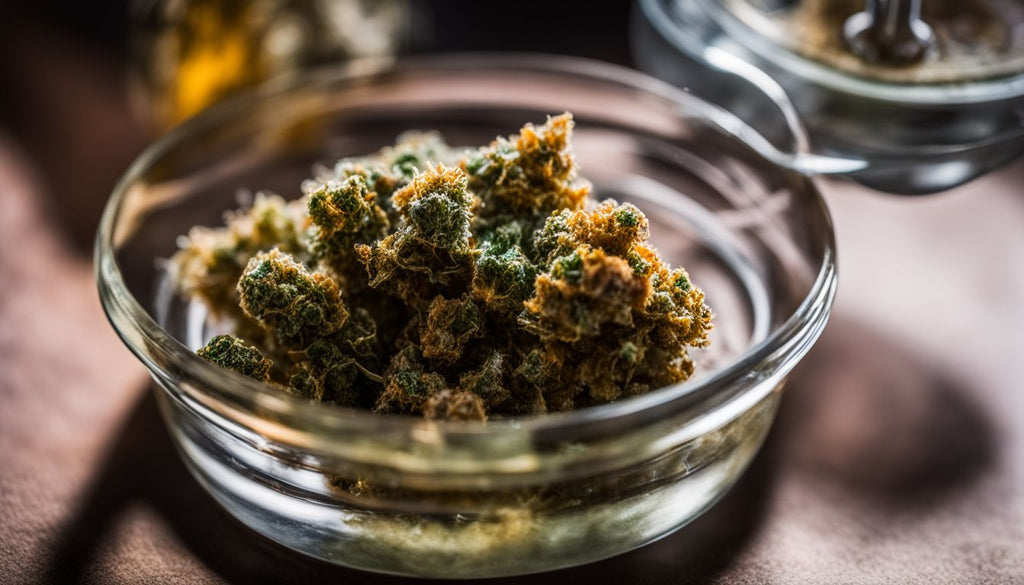

Dabs are concentrated forms of marijuana, known for their high THC potency. Extracted from cannabis plants, they come in various textures and consistencies like wax, oil, and shatter.
These concentrates deliver a powerful dose of THC, making them more potent than traditional marijuana buds. Users typically consume dabs using specialized equipment such as dab rigs or dab pens.
The connection between dabs and regular marijuana lies in the source material: both originate from the same plant. Dabbing involves heating the concentrate to vaporize it, offering an intense experience compared to smoking or vaping dried cannabis flowers.
This method highlights the evolution of cannabis consumption, catering to those seeking stronger effects from their dispensary products.
Types of Dabs
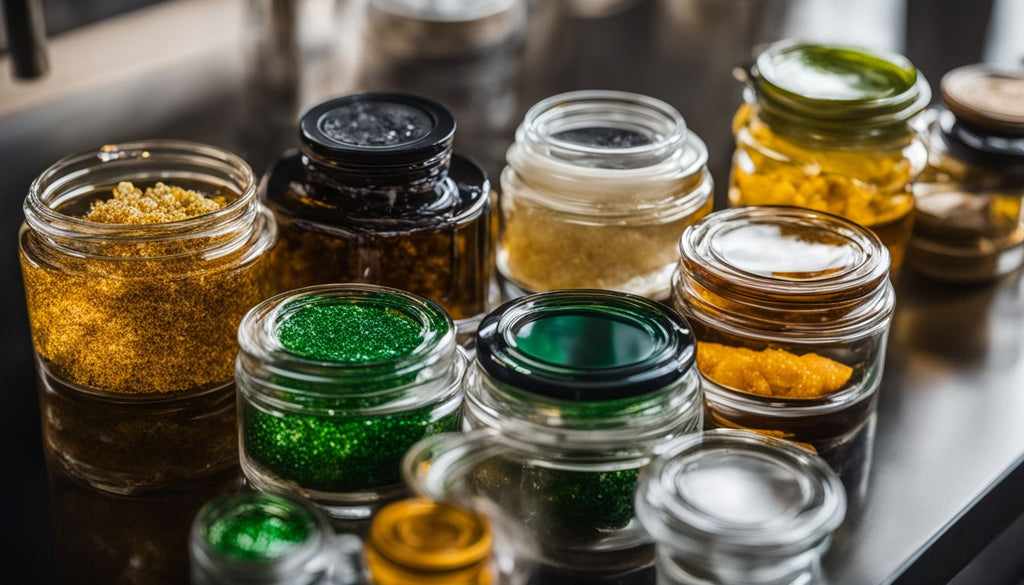

Dab oil, shatter, budder, dab wax, and live resin are popular types of dabs. Each type has its unique texture and appearance.
Dab Oil

Dab oil is a potent cannabis concentrate extracted from the marijuana plant using solvents like butane or CO2. The end product is a sticky, oily substance that ranges in color from amber to dark brown and has a thick, viscous texture.
It contains high levels of THC, the psychoactive compound in cannabis, making it incredibly potent.
During extraction, the trichomes are separated from the plant material and dissolved into the solvent to create dab oil. The result is an extremely concentrated form of THC that can be used through vaporization or dabbing methods for fast-acting effects.
Shatter

Continuing from the discussion of dab oil, shatter is another type of cannabis concentrate that has a translucent appearance and breaks into brittle, glass-like pieces. It is known for its high potency due to its pure form and typically contains higher levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) compared to other concentrates.
Shatter gets its name from its brittle texture and unique appearance, making it a popular choice among stoners looking for a potent and visually appealing concentrate.
To produce shatter, manufacturers use extraction methods such as butane hash oil (BHO) or CO2 extraction to isolate the cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material. The resulting product is then purged to remove any residual solvents, leaving behind a concentrated form of cannabis with high levels of THC.
Budder
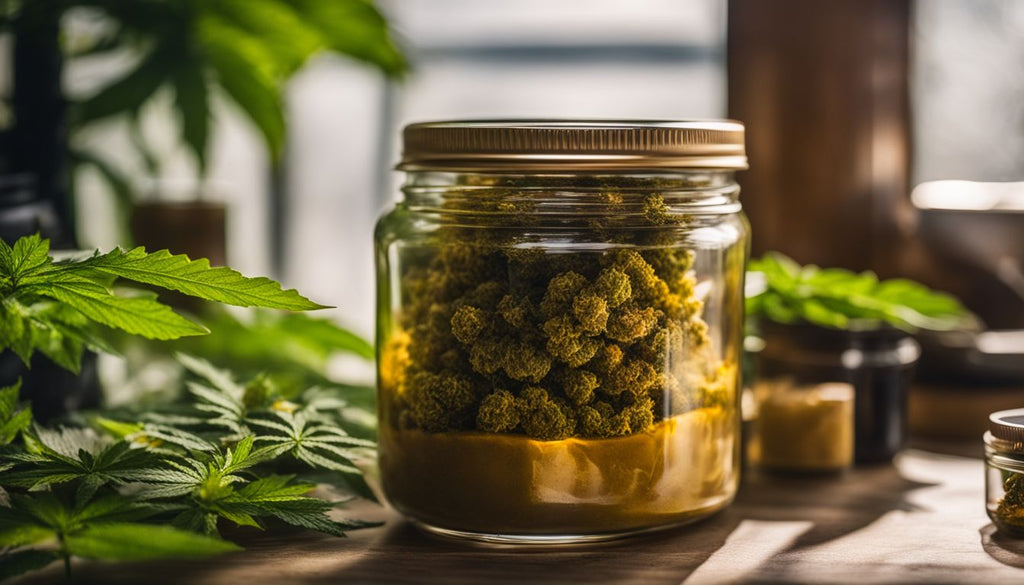

Budder is a type of cannabis concentrate known for its smooth, creamy texture and high potency. To make budder, manufacturers use solvents like butane or CO2 to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the marijuana plant.
The resulting product has a soft consistency, similar to that of butter. Budder typically contains high levels of THC, making it a popular choice for those seeking intense effects.
Its versatility allows users to dab it with a rig or vaporize it in a pen-style device.
Producing budder involves carefully controlling temperature and pressure during the extraction process. This method preserves the natural flavors and aromas of the cannabis plant, resulting in a flavorful concentrate that appeals to many consumers.
Dab Wax
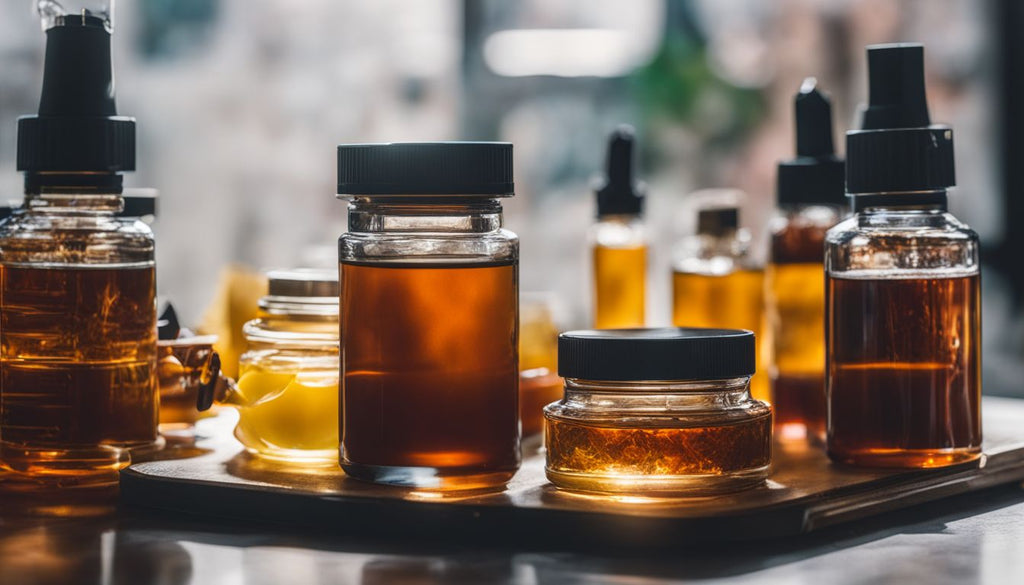

After discussing budder, let's delve into dab wax. Dab wax is a type of cannabis concentrate known for its crumbly, waxy texture. It is created using solvents like butane or CO2 to extract cannabinoids and other compounds from the cannabis plant.
The end product is a highly potent substance with a THC concentration that can reach up to 90%. Dab wax comes in various forms such as crumble, honeycomb, and butter, each offering unique textures and potencies.
When using dab wax, it's essential to start with small amounts due to its high potency.
Dabbing wax involves vaporizing the concentrate by placing it on a heated surface or nail and then inhaling the resulting vapor through a dab rig. This method allows for rapid onset effects but requires precision and caution due to the high THC content of dab wax.
Live Resin
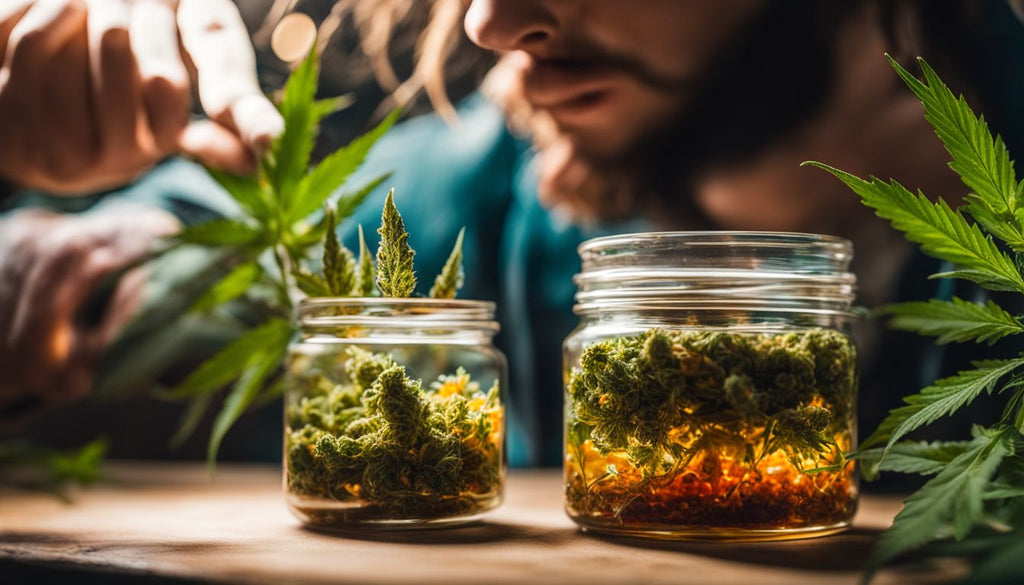

Live resin is a type of cannabis concentrate that's revered for its potent and flavorful profile. It's made using freshly harvested cannabis plants that are frozen immediately after cutting.
This freezing process helps to preserve the plant's terpene content, resulting in a concentrate with a more robust aroma and taste compared to other types of dabs. The extraction process typically involves using solvents like butane or propane to separate the trichomes from the plant material, yielding a highly concentrated product rich in cannabinoids and terpenes.
Unlike other forms of concentrates where the cannabis is dried before extraction, live resin captures the essence of the original plant, offering users a more authentic and aromatic dabbing experience.
How Dabs are Made
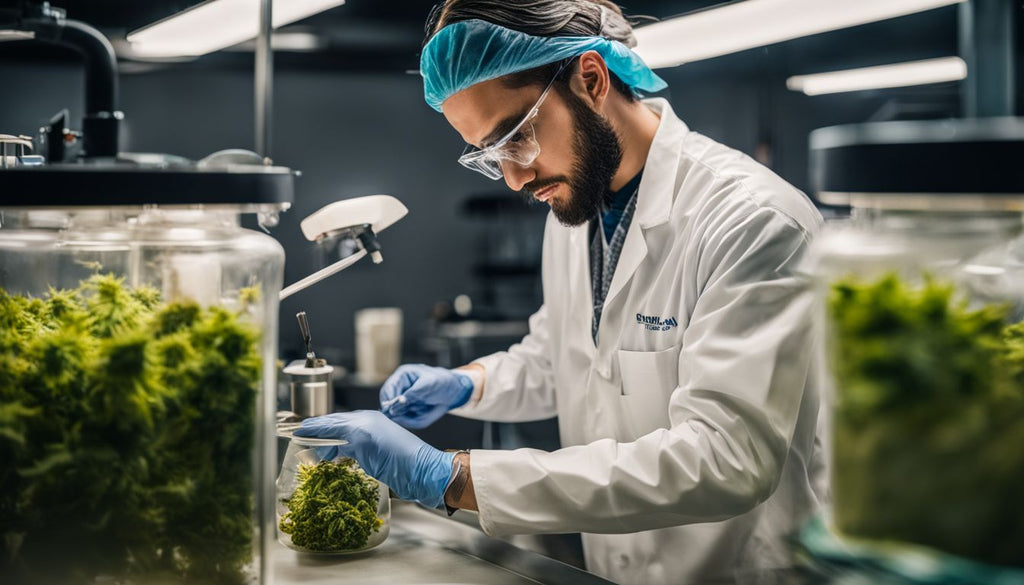

Producers use a variety of source materials, like cannabis flower or trim, to make dabs. They select from extraction methods such as butane hash oil (BHO), CO2 extraction, and solventless techniques.
Source Material

Producers use cannabis flowers and trimmings as the source material for making dabs. The plant material contains trichomes, which hold the concentrated cannabinoids and terpenes. After harvesting, the buds and trim are processed to separate the trichomes from the plant matter.
This usually involves using solvents like butane or CO2 in a controlled environment to extract the valuable compounds.
The extraction process yields a highly potent substance that becomes the base for various types of dabs such as oils, waxes, shatter, budder, and live resin. These concentrates can contain high levels of THC or CBD, offering consumers a potent experience with minimal plant material involved.
Extraction Methods

To extract dabs, producers utilize varying methods. These include:
- Butane extraction: Propane or butane is used to separate the cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material.
- CO2 extraction: This method uses pressurized carbon dioxide to extract cannabis compounds, resulting in a clean and pure concentrate.
- Rosin press: Applying heat and pressure to cannabis flower or kief yields rosin, which is solventless and preserves the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes.
- Ice water extraction: By using ice cold water, trichomes are separated from the plant material, producing hash that can be further processed into dabs.
- Solventless mechanical extraction: This method involves utilizing a series of screens or sieves to mechanically separate trichomes from plant material, resulting in solvent-free concentrates.
Post-Extraction Cleanup
After the extraction process, it's essential to ensure that the concentrate is free of any residual solvents and impurities. The post-extraction cleanup involves several crucial steps:
- Purging: After extraction, the concentrate is purged in a vacuum oven to remove any remaining solvent, ensuring a clean and safe final product.
- Winterization: This process involves using ethanol to dissolve the concentrate before freezing it. This helps to separate out waxes and lipids from the extract.
- Filtration: Filtering the winterized solution through filter paper removes any undesired particles, resulting in a smoother and more refined concentrate.
- Decarboxylation: This step activates the cannabinoids by applying heat, converting non-psychoactive THCA into THC for an enhanced experience when dabbing.
- Quality Testing: Finally, the concentrate undergoes rigorous testing for potency and purity to ensure it meets safety standards for consumption.
- Packaging: Once the concentrate has passed all quality tests, it's carefully packaged in suitable containers to preserve its freshness until use.
The Pros and Cons of Dabbing

Dabbing provides intense effects quickly and efficiently, but it may pose risks like exposure to high THC concentrations. Make an informed decision by reading the full article for a complete understanding of the pros and cons of dabbing.
Benefits
Dabbing allows for quick and potent effects, making it an ideal method for experienced cannabis users. The benefits of dabbing include:
- Fast Onset: Dabs provide rapid relief, making them effective for managing intense pain or anxiety.
- Potency: Concentrated THC offers a powerful high with minimal inhalation, perfect for those seeking strong effects.
- Flavor Profiles: Different types of dabs offer diverse terpene profiles, enhancing the taste and experience.
- Precise Dosage: Dabbing allows users to control their intake carefully, ensuring consistent effects.
Drawbacks

Using dabs can have some drawbacks, so it's important to be aware of potential issues. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Possible Health Risks: Dabbing can lead to exposure to high levels of THC, which may cause anxiety, paranoia, or even hallucinations.
- Legal Concerns: Possessing or using cannabis concentrates may not be legal in all areas, so it's crucial to know the laws in your location.
- Tolerance and Dependence: Regular dabbing can lead to increased tolerance and potential dependence on high-potency THC products.
- Safety Hazards: The process of making concentrates involves handling flammable solvents, posing risks like explosions or fires if not done correctly.
- Cost Considerations: Quality concentrates can be expensive, leading to significant costs for regular users.
Safety Considerations
When dabbing, always ensure proper ventilation in the area. Keep flammable materials away and never use dabs near an open flame. It's important to be mindful of the equipment you're using; regularly check for any cracks or damage, as this can lead to leaks or dangerous situations when handling concentrates.
Stoners should also be cautious about dosage and start with a small amount to gauge its effects before increasing consumption. Always store cannabis concentrates securely out of reach of children or pets, in child-resistant packaging if possible, and keep them away from heat sources which could cause them to degrade.
Additionally, it is crucial to remain informed about local laws regarding possession and use of marijuana concentrates.
Conclusion

After exploring the various types of dabs and how they are made, it's clear that cannabis concentrates come in a range of forms such as oils, shatter, wax, budder, and live resin. Dabbing provides potent effects but also carries some risks.
Understanding the appearance and properties of dabs is essential for those interested in this method of consuming marijuana extracts. With these insights into what dabs look like, individuals can make informed decisions about their cannabis consumption.
FAQs
1. What exactly are dabs in the world of cannabis?
Dabs are concentrated forms of cannabis extracts, like Butane Hash Oil (BHO), wax, and shatter, that deliver potent THC concentrates.
2. How do people use dabs for their effects?
People heat up these cannabis oils and extracts using a process called dabbing to inhale the vapor. This method quickly delivers dabbing effects on the brain including intense euphoria due to high THC levels.
3. Can you describe what different types of dabs look like?
Yes! BHO extracts often look like sticky oils. Wax concentrates have a soft, wax-like texture. Shatter is more solid and looks like glass that can break into pieces.
4. What materials are used to make dabs or cannabis concentrates?
To make these marijuana oils and weed dabs, producers use solvents such as butane in Butane Hash Oil (BHO) extraction methods to pull THC from the plant material.
5. Are all cannabis extracts made with chemicals?
No, not all cannabis concentrates require harsh chemicals for extraction. Some solventless methods also produce pure cannabis extracts focusing on preserving maximum potency without additional substances.